Shoulder injuries are common and can significantly impact daily activities. Rotator cuff tears are a frequent cause of shoulder pain and reduced mobility. Non-surgical treatments often help manage symptoms and enhance shoulder function. Here is more information on these injuries, the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and when to seek professional attention:
What Are Rotator Cuff Tears?
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder and allow it to move in multiple directions. A rotator cuff tear occurs when these tendons are overstretched or torn, either partially or completely. The injury can affect one or more tendons and may range from mild to severe, depending on the location and extent of the tear.
Rotator cuff tears can occur gradually over time due to repeated stress or develop suddenly in response to an injury. They may limit arm movement and cause ongoing pain if untreated. Consulting a specialist is recommended to find relief.
What Are the Causes?
Rotator cuff tears often result from repetitive shoulder use or acute injuries. Specific activities, such as throwing motions in sports or overhead work, place stress on the shoulder tendons. These repeated movements may result in wear and tear over time.
Other causes include traumatic events that involve sudden, forceful movements. These include falls or lifting heavy objects. Aging or conditions such as tendinitis may contribute to weakening tendons, increasing susceptibility to tears.
What Are the Symptoms?
Symptoms of a rotator cuff tear vary depending on the severity and type of injury. People with a partial tear may experience mild pain, while a complete tear could result in significant pain and limited shoulder function. Common signs include:
A dull ache or pain in the shoulder, especially when resting or lying on the affected side.
Weakness in the arm that makes lifting or reaching challenging.
Reduced range of motion or stiffness in the shoulder joint.
Popping or clicking sounds when moving the shoulder.
Early recognition of these symptoms can help individuals explore treatment approaches to improve shoulder function.
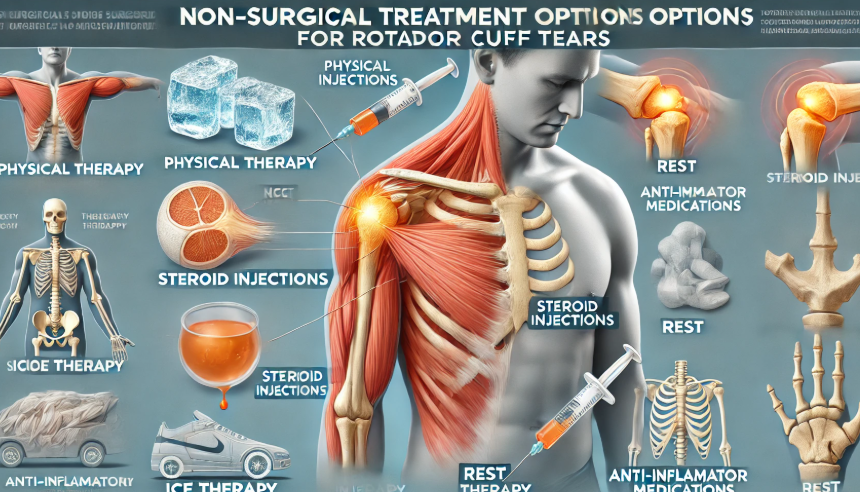
What Treatment Options Provide Relief?
Non-surgical treatments for these injuries aim to reduce symptoms such as pain and stiffness while improving shoulder mobility. These approaches provide relief and help restore functionality without invasive procedures. Here are some options you can explore with a medical professional:
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy often forms the foundation of non-surgical treatment. Tailored exercises focus on strengthening shoulder muscles, improving flexibility, and reducing pain. Guided rehabilitation programs help individuals regain full range of motion and joint stability.
Rest and Activity Modification
Avoiding activities that stress the shoulder joint helps the affected tendon rest and recover. Rest is particularly valuable for reducing inflammation and preventing further damage. Temporary adjustments, such as using a sling, may be recommended in some cases.
Medications
Over-the-counter medications can help manage pain and swelling. These include ibuprofen and other anti-inflammatory medications. They may be used in conjunction with physical therapy and other treatments.
Steroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections may be evaluated for individuals experiencing persistent pain or inflammation. While these injections do not heal the tear, they can temporarily reduce discomfort. This treatment may make it easier to engage in physical therapy exercises.
Learn More Today
Rotator cuff tears can disrupt everyday life, but non-surgical treatments effectively manage pain and improve function. From physical therapy to targeted activity modifications, there are many ways to support recovery and regain mobility. For those seeking personalized care, consulting a medical professional remains a helpful step toward finding the most suitable treatment options. Addressing shoulder concerns early is a proactive way to prioritize long-term health.